A Beginner's guide to Internet of Things(IOT)
What is IoT?
Do you remember watching C3PO and R2D2 in Star Wars for the first time and being amazed by the technology? The concept was quite novel at the time the first movies came out, but now we have bots that can do nearly everything R2 could—especially communicate, just like people.
Your smartwatch and your smartphone are basically like R2D2 and C3PO, collecting information, sharing it with each other, and communicating with other devices. That is essentially what IoT is. The Internet of Things is not one thing, but the combination of technologies that have made it possible for devices to be smart and to communicate.
Why is IoT everywhere?
The Internet of Things has done for the digital world what the invention of telephones did for the modern world. Telephones made it possible for people to share information, communicate, and pool our intellectual resources without wasting time. Similarly, IoT has made it possible for smart devices to share data with each other, making it possible to pool our digital resources for common benefits.
Now that your watch can tell your doctor what your heart rate is, and how well you sleep, any issues can be diagnosed much faster. Similarly, when sensors on vehicles tell the manufacturers exactly what issues the users are experiencing, the manufacturer can fix those issues quickly.
This not only saves time, but it also makes any process more efficient, and inexpensive. With the IoT infrastructure becoming accessible, the costs of IoT projects are also much lower than the benefits they offer. This is why tech giants like IBM, Google, Apple, and Facebook are investing heavily in IoT and its applications.
Applications of IoT
Much like web and mobile technologies, the internet of things is employed in a wide range of industries. While the applications of IoT are endless, there are certain applications that are specifically making waves across the globe. The Internet of Things being used in these industries is changing the very nature of the way these industries function. We cover some of these below, but this list is not exhaustive by any means.
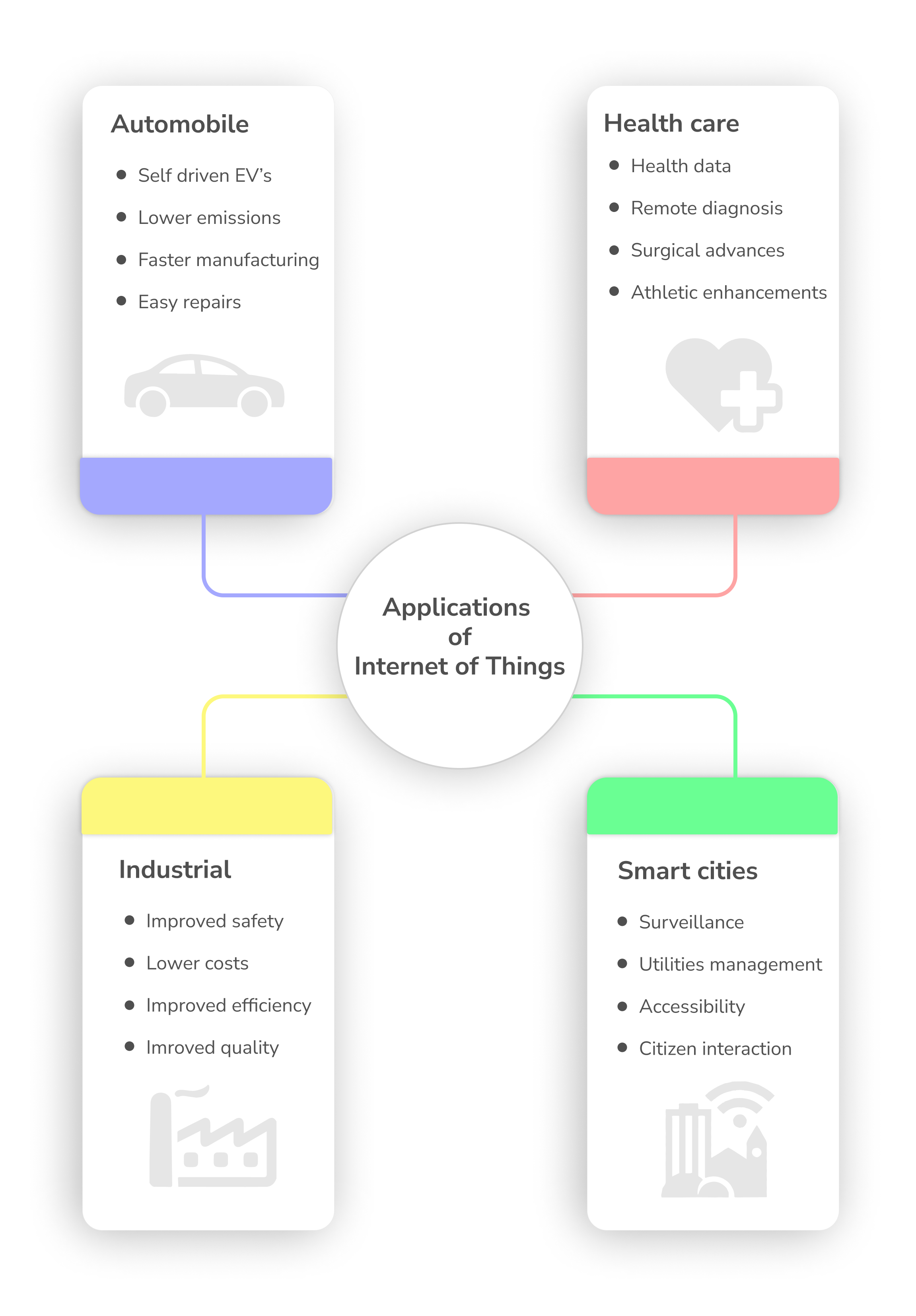
Smart Cities
With smart lights, connected power grids, smart public transport, and a security network, we are now looking at entire smart cities coming up around the world. Smart cities improve city functions, while making life easier for the citizens. But one of the biggest reasons for smart city adoption is the lowered costs and time for the city officials. With energy emissions going up every year, smart cities are a great way to curb emissions, as well as pool our resources for overpopulation.
A great example of a smart city would be New York. New York launched a smart city pilot programme in 2020, which added to its already well established surveillance infrastructure. This programme helps the city streamline traffic, detect leakages in clean water, and monitor their air quality. Similarly, Singapore has managed to haul their smart technology to make life easier for its aging population, as well as improving life for every citizen. As a result, Singapore is close to reducing its traffic to zero, and has already managed to curb overcrowding of buses by 92%. They have also digitized their healthcare system, to monitor citizen’s health and improve facilities, across the city.
All of this indicates that IoT is only going to become more prominent in our lives over the next few years.
Industrial IoT
Industrial IoT refers to smart devices such as sensors being employed for manufacturing and other industrial tasks. A very good example of IIoT is the technology developed by Siemens. Siemens uses a fully automated smart factory to create automobile parts for brands like BMW. This has reduced their overheads and made the factory much safer. They have also introduced a cloud based IoT unit named Mindsphere, which collects data from different components of the factory and analyses it to improve processes.
An ITIF report predicts that the use of IoT applications for monitoring machine health and function can improve productivity upto 25% by 2025.
Industrial IoT brings together smart devices, cloud computing, analytics, and people to improve industrial functions in manufacturing or energy.
Smart Vehicles
With Tesla making waves constantly, and EVs becoming smarter across the world, it is no surprise that smart vehicles are the future. What makes smart vehicles so much more successful are the shorter update cycles. A traditional vehicle can only be improved after getting physical feedback from tests and reviews, but smart vehicles send data back to the manufacturer constantly. This allows the automobile manufacturers to improve on the products before the customers ask for them. With brands like Tesla getting popular, the number of smart cars is projected to go upto 400 million by 2025.
IoT allows smart vehicles to be lower on maintenance as well as production costs. This is achieved by the IoT sensors on smart vehicles, which collect data and send it back for analysis. IoT adoption for vehicles also improves safety rates, as well as reduces the chances of breakdown or other issues. IoT platforms like Bytebeam can help businesses with fleet tracking, data analysis, and monitoring vehicle health.
Healthcare
The healthcare industry is likely the one industry that has benefitted the most from the advances in IoT and its infrastructure. Not only are smart devices like phones and watches a treasure trove of health data, micro sensors on personal patches or belts can also monitor glucose and blood pressure levels for at-risk patients now. These sensors are also improving precautionary healthcare, diagnostic accuracy, and athletic capabilities for professionals.
Additionally, IoT is being used in hospitals across the world for various administrative purposes. Tasks like tracking medical equipment, ensuring the supply of pharmaceuticals, deployment of medical professionals, and inventory management are being carried out with the help of IoT devices.
IoT for business
As the internet of things becomes more accessible and applicable to most industries, all industries stand to gain from the upturn in technology. IoT for business is a big leg up in terms of cost, time, and effort. The benefits are endless and are showing up in the following ways.
Smart Factories
When Henry Ford invented the modern factory layout, it revolutionized manufacturing and brought in an era of mass production. With IoT, however, factories are changing in a much bigger way.
IoT allows manufacturers to create smart factories, which are a large part of Industrial IoT. It is already an $80 billion industry, with market leaders like Shneider and Johnson & Johnson adopting IoT.
Smart factories are helping improve working conditions, making factories safer, identifying gaps and wastage, and also lowering the costs. This allows businesses to make faster updates and improve productivity, while also creating a better working environment for workers and factory personnel.
Remote Work
With IoT devices being able to collect data and analyze it easily, business leaders have a lot more insight into the working outputs of their employees. This has led to an increase in the adoption of remote work. As the pandemic pushed over 95% of the businesses to work remotely, IoT turned out to be a real-life saver, even if the switch was drastic.
The University of Hong Kong managed to employ Biofourmis’ commercial AI and IoT platform for remote monitoring of COVID-19 patients. Similarly, IoT is being used to power remote work in manufacturing, security, asset management, and other industries.
Remote work also reduces overheads and has largely improved work-life balance for people across the globe.
Data analytics
Arguably the most interesting benefit that businesses get out of IoT adoption is the data that comes in. With large amounts of data points about virtually anything, businesses can now make extremely well-informed decisions about their business. The kind of data that IoT is able to collect can accurately predict market trends, demand, efficiency, productivity, risk, and gaps.
To make it more relatable, imagine working in a cafe, and knowing exactly what the customers will order, at what time you will have the most rush, and what ingredients need to be refilled in time.
While this is a crude analogy, businesses can actually get a much deeper insight into their customer with Big Data that IoT generates, and reduce their risk potential to a minimum.
Cost and process optimization
IoT helps businesses optimize their costs and processes. So let us understand how that works with an example.
Imagine a manufacturing unit that produces bread. With IoT sensors across their production line, they can easily track the wear and tear of their machinery, repair parts in time so that production doesn’t halt, and improve inventory levels by ordering materials in time. This reduces wastage, improves speed, and ensures that there are no undesired bumps in the process.
That is how IoT works for business at any scale. Given that scalability is a major issue for any business, IoT can actually help businesses collect data that allows them to grow organically, and even take bigger risks with accurate predictions.
Challenges in IoT
As impressive as the IoT applications are today, the adoption of IoT is not without its challenges. There are several obstacles that people face when trying to inculcate IoT into their processes.
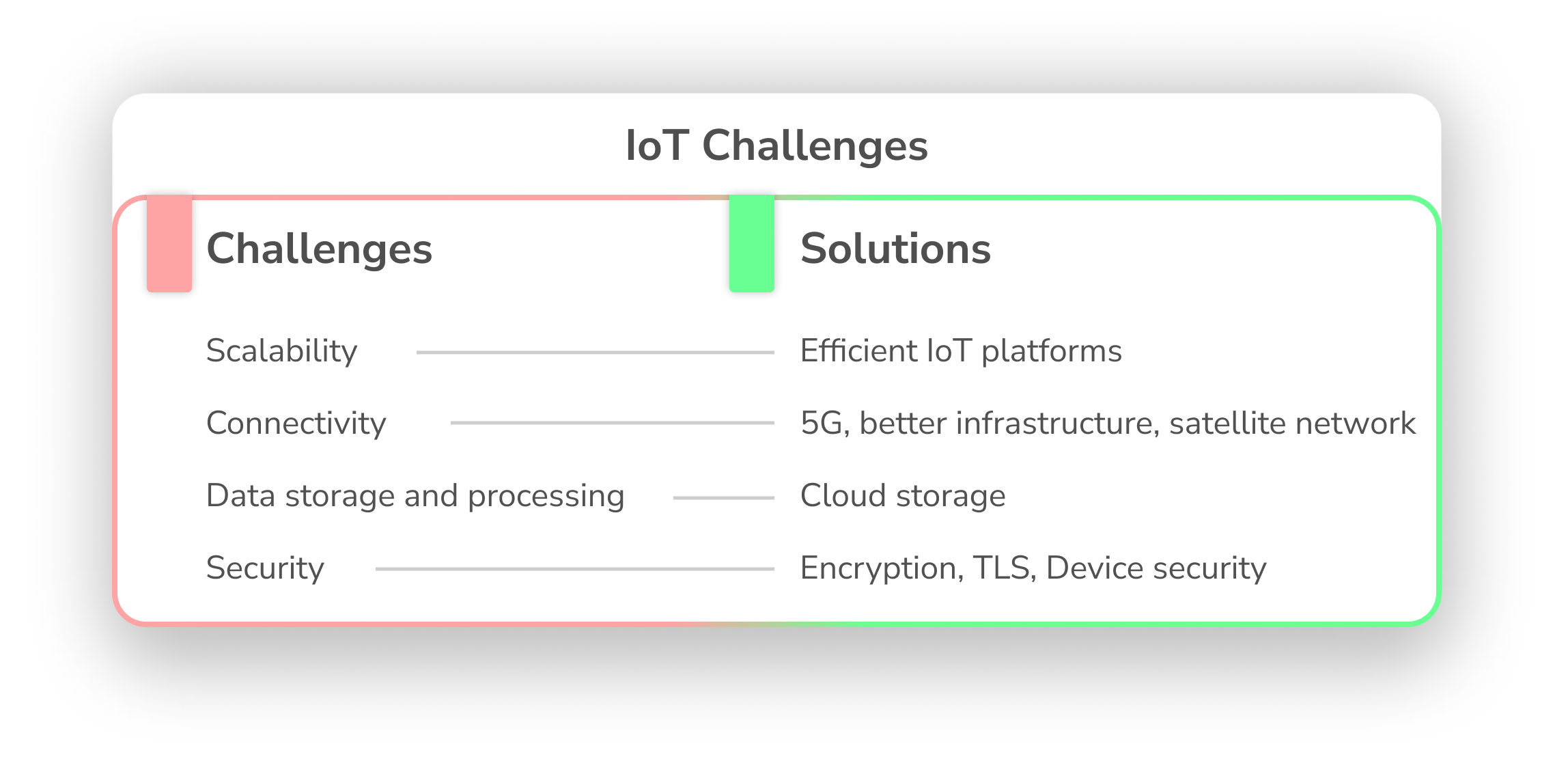
Scalability
One of the biggest challenges that businesses face is scaling IoT projects. It is easy to get a pilot project to function successfully, but to scale it to support the entire business while keeping the costs low and managing the overhaul in processes is difficult. Not to mention, IoT is a fairly new technology and experts in the field are not common. This makes the process of scaling IoT projects that much more difficult. Microsoft’s report on IoT explains the challenges and trends in further detail.
Thankfully, there are solutions that are designed specifically for businesses to be able to scale their IoT projects. Solutions like Bytebeam focus on providing a single platform for all IoT-related functions so that businesses can focus on growing their projects rather than fiddling with scalability.
Connectivity
As common as IoT is across the globe by now, connectivity is still an issue, in more ways than one. Firstly, a lot of remote areas still do not have internet connectivity. This is especially relevant to IIoT projects because a lot of manufacturing or energy units are located in remote areas. Sensors may not relay accurate information if the connectivity on the devices is poor, which affects the entire project. Another common issue is that connectivity is especially patchy when the devices are on the move.
Satellite internet solutions are quickly remedying this issue, but the costs for connectivity are still not entirely accessible.
Data Storage
IoT sensors can generate a LOT of data. A single smart device roughly generated over 2011 GB of data in 2019. This number is expected to grow by over 400% by 2025. Industrial data is far higher than the average, so data storage is obviously a challenge for businesses.
Building a data center that can handle this scale of data is not for the faint of the heart. Most IoT companies instead rely on cloud providers for data storage. But even with cloud solution offerings managing cost & archiving older data to cheaper storage solutions is far from trivial. So finding a stable ground with data storage is a slightly tedious task.
Data Processing
Now imagine if storing several petabytes of data is a challenge, how much of a headache the processing of this data can be. Without the right processing and analysis solutions, these metaphorical truckloads of data can prove to be pointless. Microsoft Azure’s IoT signals report found that data storage and processing are still a core challenge for various businesses.
Additionally, data science is a discipline where asking the right questions is as important as getting the right answers. Unless businesses have specific streamlined goals, data insights can be irrelevant and data processing remains a challenge for deploying IoT projects successfully.
Security and privacy
As with any advanced technology, IoT faces a lot of scrutinies when it comes to security. As IoT is a fairly new technology, the security protocols are still evolving, and as the technology advances, so do the threats. One of the major concerns for IoT is that given how seamlessly collects data, it might threaten any privacy concerns. For example, smartphone users often get targeted ads for their location, and as very few people care to go through the terms and conditions, they consider it an invasion of privacy.
There are several aspects to security in terms of IoT and we will look at them one by one.
Endpoint security
When all your devices are connected, any device can be used to breach security, including sensors, connected appliances, or even cameras. These devices can be breached using open ports or unsecured components, and the breach of one device can snowball into a major security threat.
This is why endpoint security is crucial to secure IoT devices. Endpoint security includes regular maintenance of devices, using secure networks, frequent updates, and strong passwords, among other things.
Server security
Server security is absolutely essential for any business, given that primary servers offer a big risk-big reward temptation. Hackers often target the servers directly through malware attacks or network breaches.
This also applies to the cloud, as native cloud breaches are one of the most common threats. When transferring data to the cloud, it is important to make sure that the data is encrypted and the connection is secure. All of this can be done by employing security professionals or using cybersecurity tools.
Encryption
Encryption at all levels is practically a basic requirement for security. Encryption ensures that even if any important data is stolen, it is useless to the hackers. Protocols like SFTP and TLS ensure that your data communication is encrypted and secured, so it is always good to employ these.
Data laws and regulations
Every country and region has its own data regulations. The EU requires GDPR compliance, while several American companies need to be CCPA compliant. These laws specifically define how and what data can be collected, which data can be used or distributed, and how the data needs to be stored.
Anyone doing business in these regions needs to be aware of these compliances, otherwise, they could face legal action.
IoT development
The internet of things is largely understood as the sum of its hardware parts. But what truly makes these devices ‘smart’ is connectivity and the cloud infrastructure behind these devices. Joining the hardware, connectivity, and cloud parts is what IoT development is all about.
For instance, a smart car might have all the right hardware for it to be able to drive itself, check GPS, avoid accidents, check maintenance, and monitor device health, but it will not be able to do any of that without tons of data being collected behind the scenes and AI/ML models being trained.
IoT platforms
There are three parts to the overall IoT infrastructure—the devices, the firmware, and the cloud software. The devices are the ones that collect data, the firmware on the devices are the algorithm that helps the device function in a particular manner, and the cloud software is what gathers and analyzes the data, and runs the show. Now the software part of it could be cloud-based, as it usually is. And this third part, the cloud infrastructure, is what brings the entire process together.
It is not enough to simply collect the data, you need the right data, which has to be organized, analyzed, and used in the right way. This is where IoT platforms come in. Platforms such as Bytebeam help you create backend applications that allow you to monitor your devices remotely, check on their performance and health, and even make sense of the data that you collect.
Without the right IoT platform, the amount of data generated makes very little difference. Because the right IoT platform is the tool that is required to reign in the absolute chaos of big data. IoT platforms also allow you to deploy updates to your device, without having to physically work on them.
Complementary technologies
The beauty of the internet of things is how many technologies it is compatible with. IoT is not only an asset by itself, but it also powers several other technologies and is helped by many too. Some of these technologies are so integral to IoT, that they are considered a part of IoT itself. Let us take a look at these technologies that are making almost as many waves as IoT.
Edge Computing
Edge computing is literally a distribution of computing capabilities to the edge. Imagine any system, there is a server, and several devices that are connected to it. Now traditional processes would use devices to collect the data, but the data was transferred back to the server in order to be processed. A more relatable example would be automated traffic signals. Cities like Singapore have automated traffic signals that can gauge the traffic volumes and adjust the signal time and frequency accordingly, while also syncing with other signals around it to maintain a steady flow of traffic. All of this is done without the traffic sensors sending any data back to the servers for computing the best solution.
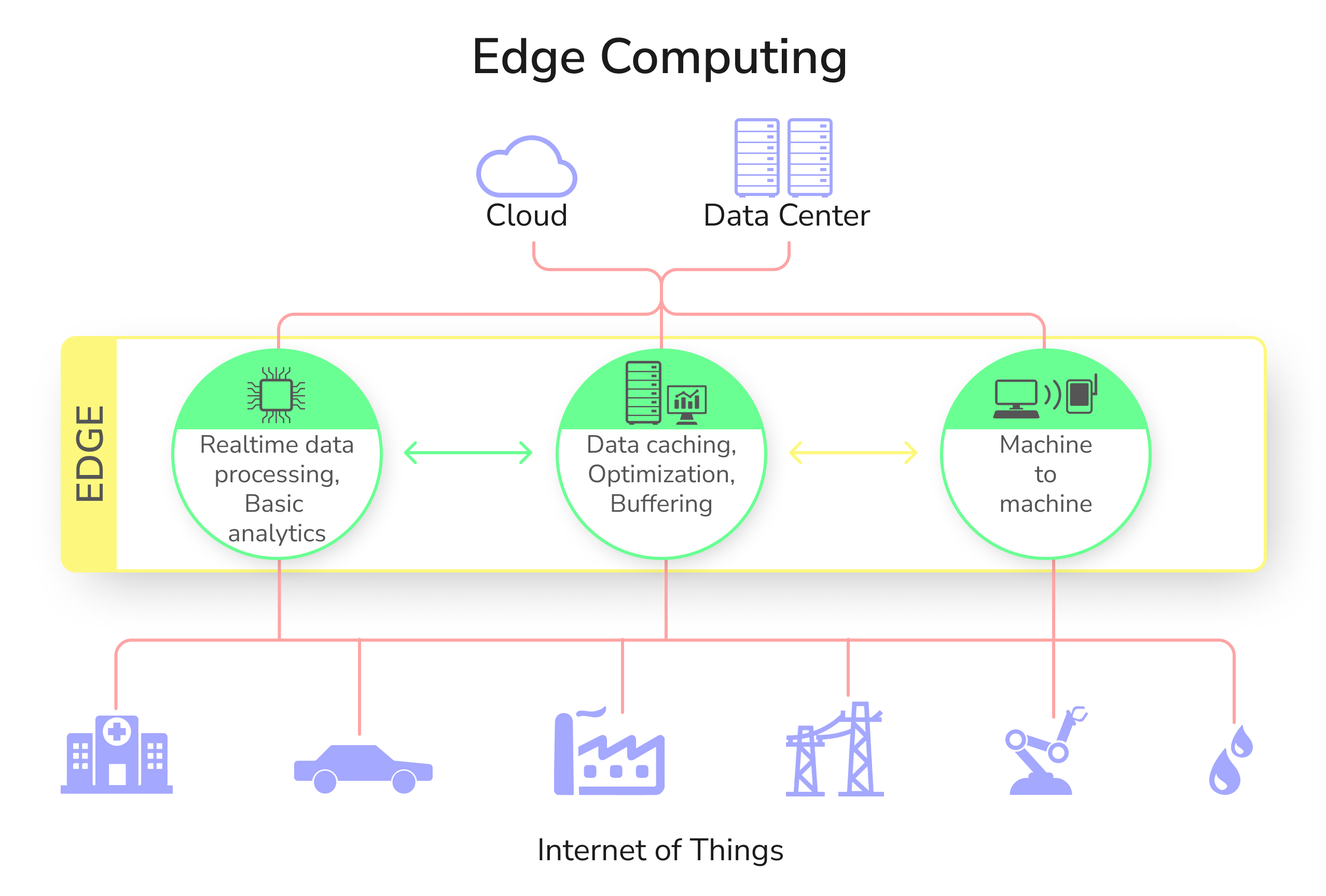
With edge computing, each device, however remote, has at least limited processing power. This overrides several connectivity issues, as well as improves the speed of any process massively.
Cloud computing
Cloud computing is less of a technology and more of an update in how systems function. Put simply, cloud computing takes all the essential parts of a system, i.e. servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence, and puts them up on the internet.
The biggest advantage of this is that it lowers data storage costs, improves flexibility, and helps businesses scale easily.
5G
Remember a time when you had to wait for a single webpage to load for around a minute? Very few people do. But imagine going from there, to streaming HD videos on your phone seamlessly. This is possible because of the network updates that we have witnessed in the last decade.
5G is the fifth generation technology standard for broadband cellular networks. 5G is the reason why mobile devices now enjoy unprecedented internet speeds. Given that connectivity is one of the key requirements for smart devices, 5G has opened up several opportunities for IoT.
AI/ML
Artificial intelligence and Machine Learning are perhaps the most complementary technologies to IoT. Both AI and ML require copious amounts of data to function. Machine learning algorithms rely on data patterns, and Artificial Intelligence is trained based on empirical data. This is what makes IoT such an incredible asset for both these technologies. Several applications of IoT actively involve AI and ML, like drones that are trained to locate garbage on the shorelines or facial recognition technologies that can be used to identify threats.
Industry 5.0 and IoT
Industry 5.0 is the next stage of industrialization and a natural successor to Industry 4.0. While Industry 4.0 focused on the collaboration of technologies, Industry 5.0 is focused upon the collaboration between people and technologies.
The core tenet of Industry 5.0 is leveraging technology to improve human lives, and IoT stands at the center of this stage. By leveraging smart technology, edge computing, and interconnectedness, machines can be used to find the optimal balance between efficiency and productivity.
Takeaways
All of this tells us that IoT is not just a trend or a buzzword, it is a robust technology that is here to stay and grow. There are several aspects of the technology that are still unfolding and solutions like Bytebeam are helping businesses keep up with the rapid advancement of the industry. If you’d like to learn more about Bytebeam and our solutions, feel free to reach out or comment.
FAQs
What is an IoT device?
An IoT device is any smart device that can communicate with other devices through sensors and internet networks. These devices are crucial to the internet of things as they bridge the gap between the digital and the physical in IoT.
What are some examples of IoT?
The most common examples of IoT are wearables. The Fitbit, Apple watch, glucose patches, or even a pedometer is a good example of wearable IoT devices. These devices collect data, and the data is then used to improve a particular function. Examples of IoT range from garbage detecting drones, to facial recognition cameras, as the applications of IoT are endless.
Why does IoT matter?
The internet of things is one of the technologies that is enabling the human-machine connect. IoT applications improve human lives on several levels. It is used in absolutely crucial solutions like surgery and diagnostics, as well as for economic purposes like collecting user preferences for business. IoT improves existing systems significantly as it provides specific data about any function or activity we require.